Breast Cancer in Nepal: Understanding, Prevention and Survival
Breast cancer is a significant health concern worldwide and Nepal is no exception. It is essential to spread awareness about breast cancer, its types, causes, symptoms and available treatments. This article aims to provide a complete overview of breast cancer in Nepal.
Types of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can manifest in various forms, with the most common types being:
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): A non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells are found in the lining of a breast duct but have not spread.
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): The most common type, where cancer cells spread beyond the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Cancer that starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules) and can spread to other parts of the body.
- Triple-negative Breast Cancer: A type that lacks three commonly found receptors in breast cancer, making it more challenging to treat.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer: A rare and aggressive type that blocks lymph vessels in the breast, leading to redness and swelling.
Causes and Symptoms of Breast Cancer
Understanding the causes and symptoms of breast cancer is crucial for early detection and treatment:
Causes:
- Genetic Factors: Family history and inherited gene mutations (like BRCA1 and BRCA2).
- Hormonal Influence: Hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptives and early menstruation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, alcohol consumption and lack of physical activity.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to radiation and certain chemicals.
Symptoms:
- A lump or thickening in the breast or underarm.
- Change in size, shape or appearance of the breast.
- Nipple discharge, often bloody.
- Redness or pitting of the breast skin.
- Pain in the breast or nipple area.
Diagnosis and Tests
To diagnose breast cancer, doctors use several tests:
- Mammogram: X-ray of the breast to detect tumors.
- Ultrasound: Sound waves to create images of the breast tissue.
- Biopsy: Removing a small tissue sample for lab analysis.
- MRI: Detailed images of the breast using magnetic fields.
- Genetic Testing: To identify mutations in genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2.
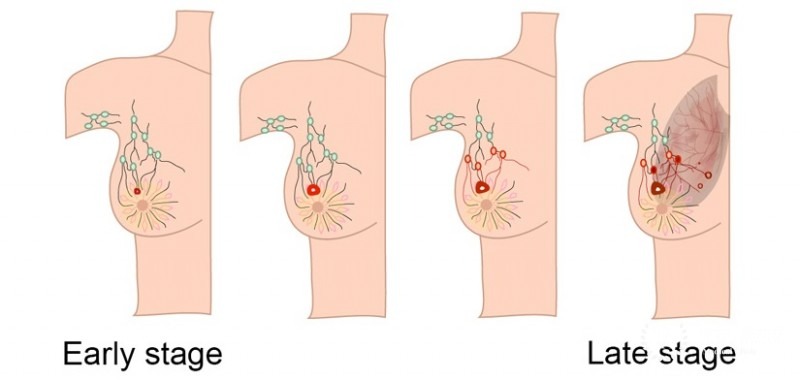
Stages of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is categorized into stages based on the size of the tumor and its spread:
- Stage 0: Non-invasive, confined to ducts or lobules.
- Stage I: Small tumor (up to 2 cm) with no lymph node involvement.
- Stage II: Larger tumor (2-5 cm) or cancer spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: Tumor larger than 5 cm or cancer spread to multiple lymph nodes or nearby tissues.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastatic breast cancer).
Treatment for Breast Cancer
The treatment plan depends on the type and stage of breast cancer:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor (lumpectomy) or entire breast (mastectomy).
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs that target and destroy cancer cells.
- Hormone Therapy: Blocking hormones that fuel cancer growth.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific characteristics of cancer cells.
Side Effects of Breast Cancer Treatment
Treatment for breast cancer can lead to various side effects:
- Surgery: Pain, swelling and scarring.
- Radiation Therapy: Skin irritation, fatigue and breast swelling.
- Chemotherapy: Nausea, hair loss, fatigue and increased infection risk.
- Hormone Therapy: Hot flashes, mood swings and risk of osteoporosis.
- Targeted Therapy: Diarrhea, liver problems and heart issues.
Can Breast Cancer Be Prevented? How to Lower the Risk?
While there’s no sure way to prevent breast cancer, certain lifestyle changes can lower the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Alcohol consumption is linked to a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Stay Physically Active: Regular exercise can help lower the risk.
- Breastfeed: Breastfeeding for several months can reduce the risk of breast cancer.
- Avoid Hormone Replacement Therapy: Use it only if necessary and under medical advice.
What is the Survival Rate for Breast Cancer?
The survival rate for breast cancer varies based on the stage at diagnosis and treatment effectiveness. In developed countries, the 5-year survival rate is around 91%. But in Nepal, it may be lower due to limited access to early diagnosis and treatment. However, with increasing awareness and better healthcare facilities, the survival rate for breast cancer in Nepal is improving.
How Long Do Breast Cancer Patients Live?
The life expectancy of breast cancer patients depends on several factors, including the stage at diagnosis, type of cancer and overall health. Many patients live long and healthy lives after treatment, especially if the cancer is detected early.
How to Check Breast Cancer at Home?
Self-examination is vital for early detection. Here’s how to do it:
- Visual Inspection: Stand before a mirror and check for any changes in breast shape, size, or skin texture.
- Manual Examination: Use your fingers to feel for lumps or thickening in the breast and underarm, both while lying down and standing up.
- Check Nipples: Gently squeeze your nipples to check for any discharge.
It’s important to note that self-examination should not replace regular screenings by a healthcare professional.
Breast cancer in Nepal is a growing concern, but with increased awareness, early detection and proper treatment, the outcomes can be significantly improved. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle and understanding the risk factors can go a long way in lowering the risk of breast cancer.