Dilation and Curettage (D&C): What You Need to Know About the Procedure and Recovery
Dilation and Curettage, commonly known as D&C, is a surgical procedure that involves removing tissue from the inside of the uterus. This procedure is often recommended by doctors for various reasons, such as diagnosing or treating certain uterine conditions, or after a miscarriage. Here’s a simple guide to help you understand what D&C is, why it’s done, and what to expect during and after the procedure.
What is Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
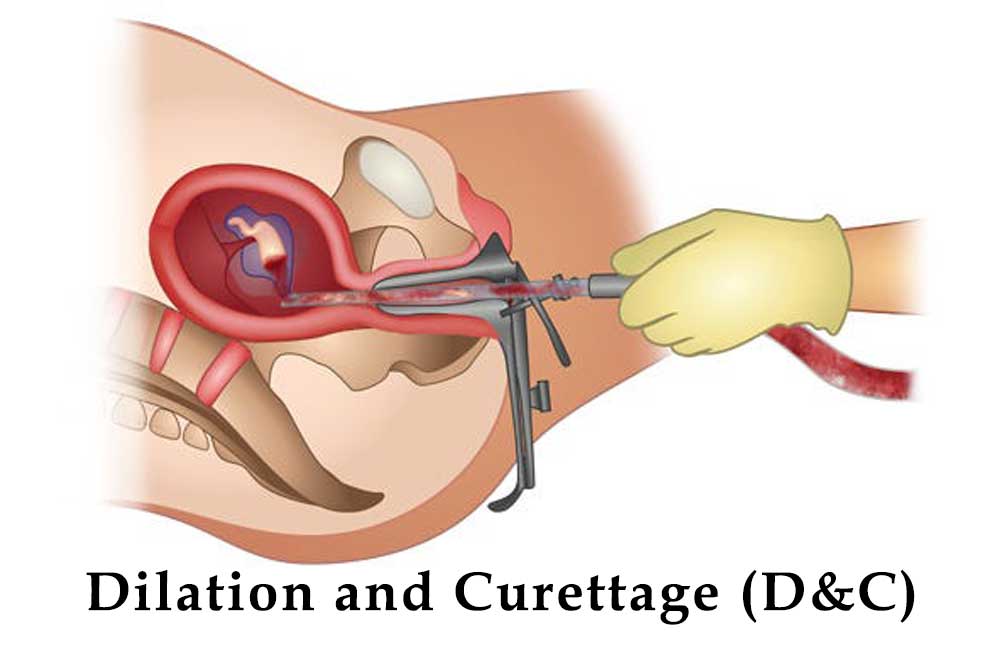
D&C is a minor surgical procedure where a doctor removes tissue from the lining of the uterus (endometrium). The procedure involves two main steps:
- Dilation: The cervix (the lower part of the uterus) is gently opened or dilated.
- Curettage: A small instrument called a curette is used to remove tissue from the uterine lining.
D&C is typically performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s situation and the doctor’s recommendation.
Why is D&C Performed?
D&C can be done for several reasons, including:
- Diagnosing Uterine Conditions: D&C is often used to diagnose conditions like uterine polyps, fibroids, or cancer by collecting tissue samples.
- Treating Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: It can help stop heavy or irregular bleeding by removing the thickened lining of the uterus.
- After a Miscarriage: D&C may be performed to remove any remaining tissue in the uterus after a miscarriage, preventing infection and complications.
- Managing Postpartum Bleeding: In some cases, D&C is used to remove any retained placental tissue after childbirth.
What to Expect During the Procedure
D&C is usually a short procedure that lasts about 15 to 30 minutes. Here’s what typically happens:
- Preparation: Before the procedure, you may be given anesthesia. Depending on the type, you might be awake (with local anesthesia) or asleep (with general anesthesia).
- Dilation: The doctor will gently dilate your cervix to allow access to the uterus.
- Curettage: Using a curette, the doctor will carefully scrape away the uterine lining or remove the necessary tissue.
- Recovery: After the procedure, you’ll be taken to a recovery room where you’ll be monitored until the anesthesia wears off. You can usually go home the same day.
Recovery After D&C
Recovery from D&C is usually quick, but it’s important to take care of yourself. Here are some tips:
- Rest: Take it easy for a day or two after the procedure. Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities.
- Manage Pain: Mild cramping and spotting are normal after D&C. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help ease discomfort.
- Watch for Complications: Contact your doctor if you experience heavy bleeding, severe pain, fever, or foul-smelling discharge, as these could be signs of complications.
- Follow-up: Make sure to attend any follow-up appointments to ensure your recovery is on track.
Potential Risks of D&C
While D&C is generally safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks. These may include:
- Infection: There's a small risk of infection after the procedure.
- Heavy Bleeding: Rarely, D&C may cause heavy bleeding that requires further treatment.
- Perforation: In rare cases, the instrument used during the procedure may puncture the uterus.
Your doctor will discuss these risks with you and answer any questions you may have before the procedure.
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a common and generally safe procedure used to diagnose and treat various uterine conditions. Understanding what to expect during and after the procedure can help you feel more prepared and at ease. If you have any concerns or need more information, be sure to talk to your doctor—they are there to guide you through every step of the process.