Fertility diagnosis for Male and Female
Fertility diagnosis for male Semen analysis:
A sample may be taken to test for sperm concentration, motility, color, quality, any infections, and whether any blood is present. Sperm counts can fluctuate, so that several samples may be necessary.
- Blood test: The lab will test for levels of testosterone and other hormones.
- Ultrasound: This may reveal issues such as ejaculatory duct obstruction or retrograde ejaculation.
- Chlamydia test: Chlamydia can affect fertility, but antibiotics can treat it.
Fertility diagnosis for female
- Blood test: This can assess hormone levels and whether a woman is ovulating.
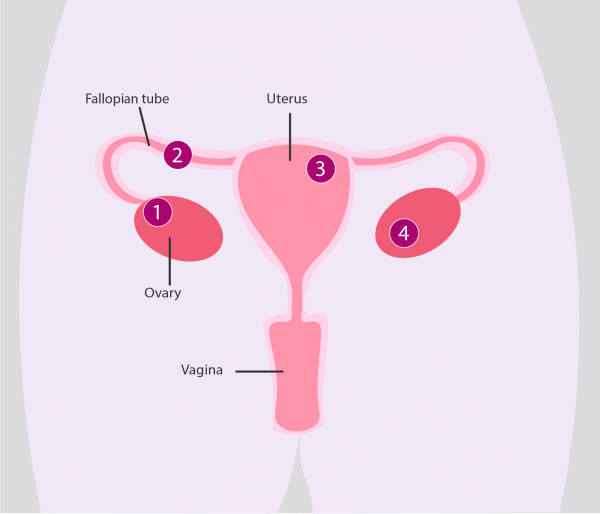
- Hysterosalpingography: Fluid is injected into the woman’s uterus and X-rays are taken to determine whether the fluid travels properly out of the uterus and into the fallopian tubes. If a blockage is present, surgery may be necessary.
- Laparoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the abdomen and pelvis, allowing a doctor to look at the fallopian tubes, uterus, and ovaries. This can reveal signs of endometriosis, scarring, blockages, and some irregularities of the uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Ovarian reserve testing, to find out how effective the eggs are after ovulation.
- Genetic testing, to see if a genetic abnormality is interfering with fertility
- Pelvic ultrasound, to produce an image of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
- Chlamydia test, which may indicate the need for antibiotic treatment.
- Thyroid function test, as this may affect the hormonal balance.