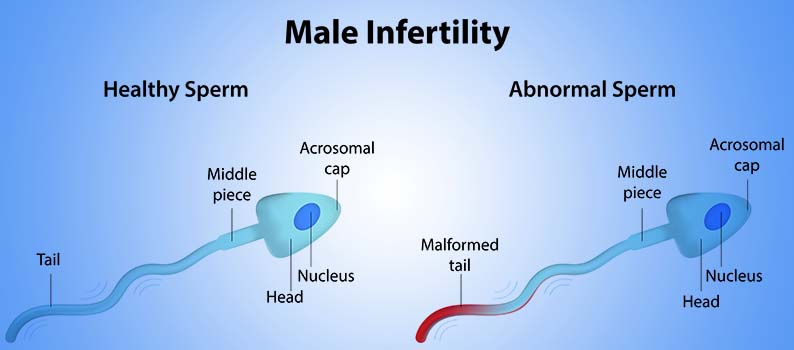
Male infertility means a man is not able to start a pregnancy with his female partner.
About 13, out of 100 couples, can’t get pregnant with unprotected love making. There are many causes for infertility in men and women. This is most often due to problems with his sperm production or with sperm delivery.
Causes of Male Infertility:
Making mature, healthy sperm that can travel depends on many things. Problems can stop cells from growing into sperm. Problems can keep the sperm from reaching the egg. Even the temperature of the scrotum may affect fertility.
These are the main causes of male infertility:
- Sperm Disorders
- Varicoceles
- Retrograde Ejaculation
- Immunonologic Infertility
- Obstruction
- Hormones
- Medication
Sperm Disorders
The most common problems are with making and growing sperm. Sperm may:
- not grow fully
- be oddly shaped
- not move the right way
- be made in very low numbers (oligospermia)
- not be made at all (azoospermia)
Sperm problems can be from traits you’re born with. Lifestyle choices can lower sperm numbers. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking certain medications can lower sperm numbers. Other causes of low sperm numbers include long-term sickness (such as kidney failure), childhood infections (such as mumps), and chromosome or hormone problems (such as low testosterone).
Damage to the reproductive system can cause low or no sperm. About 4 out of every 10 men with total lack of sperm (azoospermia) have an obstruction (blockage) within the tubes the sperm travel through. A birth defect or a problem such as an infection can cause a blockage.
Varicoceles
Varicoceles are swollen veins in the scrotum. They’re found in 16 out of 100 of all men. They are more common in infertile men (40 out of 100). They harm sperm growth by blocking proper blood drainage. It may be that varicoceles cause blood to flow back into your scrotum from your belly. The testicles are then too warm for making sperm. This can cause low sperm numbers.
For more information please refer to the Varicoceles information page.
Retrograde Ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation is when semen goes backwards in the body. They go into your bladder instead of out the penis. This happens when nerves and muscles in your bladder don’t close during orgasm (climax). Semen may have normal sperm, but the semen is not released from the penis, so it cannot reach the vagina.
Retrograde ejaculation can be caused by surgery, medications or health problems of the nervous system. Signs are cloudy urine after ejaculation and less fluid or “dry” ejaculation.
Immunologic Infertility
Sometimes a man’s body makes antibodies that attack his own sperm. Antibodies are most often made because of injury, surgery or infection. They keep sperm from moving and working normally. We don’t know yet exactly how antibodies lower fertility. We do know they can make it hard for sperm to swim to the fallopian tube and enter an egg. This is not a common cause of male infertility.
Obstruction
Sometimes the tubes through which sperm travel can be blocked. Repeated infections, surgery (such as vasectomy), swelling or developmental defects can cause blockage. Any part of the male reproductive tract can be blocked. With a blockage, sperm from the testicles can’t leave the body during ejaculation.
Hormones
Hormones made by the pituitary gland tell the testicles to make sperm. Very low hormone levels cause poor sperm growth.
Chromosomes
Sperm carry half of the DNA to the egg. Changes in the number and structure of chromosomes can affect fertility. For example, the male Y chromosome may be missing parts.
Medication
Certain medications can change sperm production, function and delivery. These medications are most often given to treat health problems like:
- arthritis
- depression
- digestive problems
- anxiety or depression
- infections
- high blood pressure