Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and Its Effects on Women
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects many women of reproductive age. It is important to understand this condition as it can have a significant impact on a woman’s health and well-being.
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
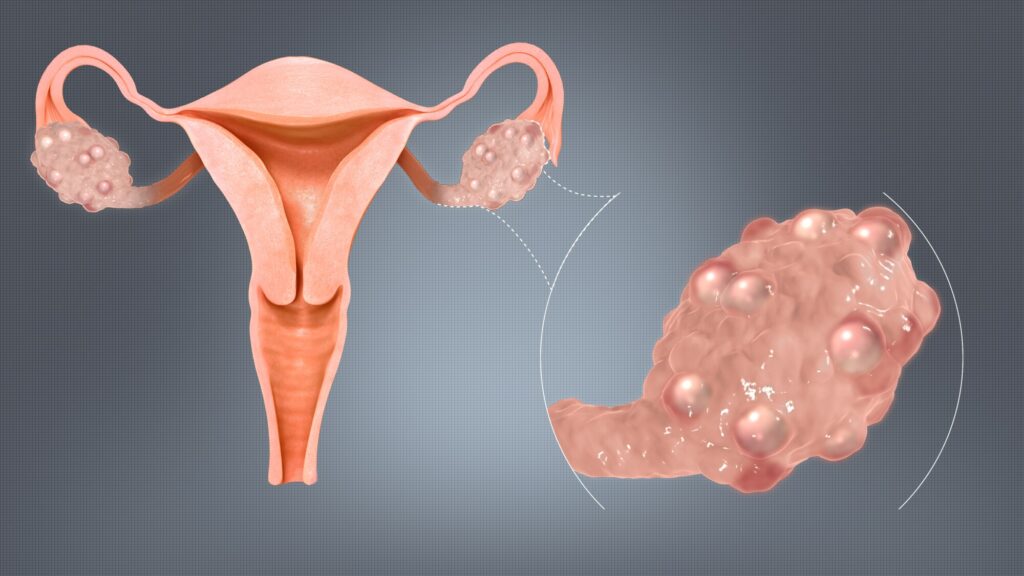
PCOS is a condition marked by a hormonal imbalance due to the excessive creation of hormones. If you have PCOS, your ovaries produce unusually high levels of hormones called androgens. This causes your reproductive hormones to become imbalanced, leading to irregular menstrual cycles and the presence of cysts on the ovaries. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it is believed to be related to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances. Women with PCOS may produce higher levels of male hormones, which can lead to symptoms like excess facial and body hair, acne, and hair loss.
What is the main reason behind PCOS?
The main reason behind PCOS is not fully understood. However, it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin is also a significant factor.
What are the four stages of PCOS?
PCOS can be categorized into four different types based on the dominant symptoms:
- Insulin-resistant PCOS: Characterized by insulin resistance and obesity.
- Post-pill PCOS: Occurs after discontinuing birth control pills.
- Inflammatory PCOS: Linked to chronic inflammation.
- Adrenal PCOS: Associated with an overproduction of androgens by the adrenal glands.
Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary widely but often include:
- Irregular periods or no periods at all
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Abnormal hair growth on the face and body
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain and difficulty losing weight
- Thinning hair on the scalp
- Darkening of the skin, particularly around the neck, groin, and under the breasts
- Presence of cysts on the ovaries
- Infertility
Diagnosis of PCOS
PCOS is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests and ultrasound imaging of the ovaries. Doctors look for at least two of the following criteria:
- Irregular ovulation
- High levels of androgens
- Presence of cysts on the ovaries
Treatment for PCOS
The treatment for PCOS focuses on managing symptoms and may include lifestyle changes, medication and sometimes surgery. Common treatments include:
- Birth control pills to regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels
- Metformin to improve insulin resistance
- Medications to stimulate ovulation for those trying to conceive
- Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise
Is PCOS painful?
PCOS itself is not usually painful but the symptoms associated with it such as heavy periods and ovarian cysts can cause discomfort and pain.
Is PCOS a lifetime disease?
PCOS is considered a chronic condition meaning it can last a lifetime. However, the symptoms can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
Who is mostly affected by PCOS?
PCOS mostly affects women of reproductive age typically between the ages of 15 and 44. It can affect women of all races and ethnicities.
How does PCOS affect women’s mental health?
PCOS can significantly impact a woman’s mental health. The symptoms such as weight gain, acne and excess hair growth can affect self-esteem and lead to anxiety and depression.
Can one live a normal life with PCOS?
Yes, many women with PCOS can live normal healthy lives with proper management and treatment of their symptoms.
Does PCOS get worse with age?
PCOS symptoms may change with age. While some symptoms may improve after menopause, others such as insulin resistance and risk of heart disease, may worsen.
Can women with PCOS get pregnant?
Yes, women with PCOS can get pregnant although they may have difficulty due to irregular ovulation. Treatments are available to help improve fertility.
What is the primary goal of treatment for PCOS?
The primary goal of treatment for PCOS is to manage symptoms, reduce the risk of long-term health complications and improve quality of life.
Is PCOS genetic?
Researchers are discovering more about PCOS. Some evidence shows PCOS has a genetic or hereditary component. This means if your biological parent has PCOS, you may be more likely to have it too.
What happens if you ignore PCOS?
If PCOS is ignored, it can lead to serious health issues such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to manage its symptoms and prevent long-term health issues. With proper treatment and lifestyle changes, women with PCOS can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.