Understanding the Menstrual Cycle: A Complete Guide to Its Phases, Symptoms, and Hormones
The menstrual cycle is a natural process in a woman's body. It prepares her for a possible pregnancy. Understanding this cycle can help women manage their health better. This guide will explain the phases, symptoms, and hormonal changes in simple terms.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
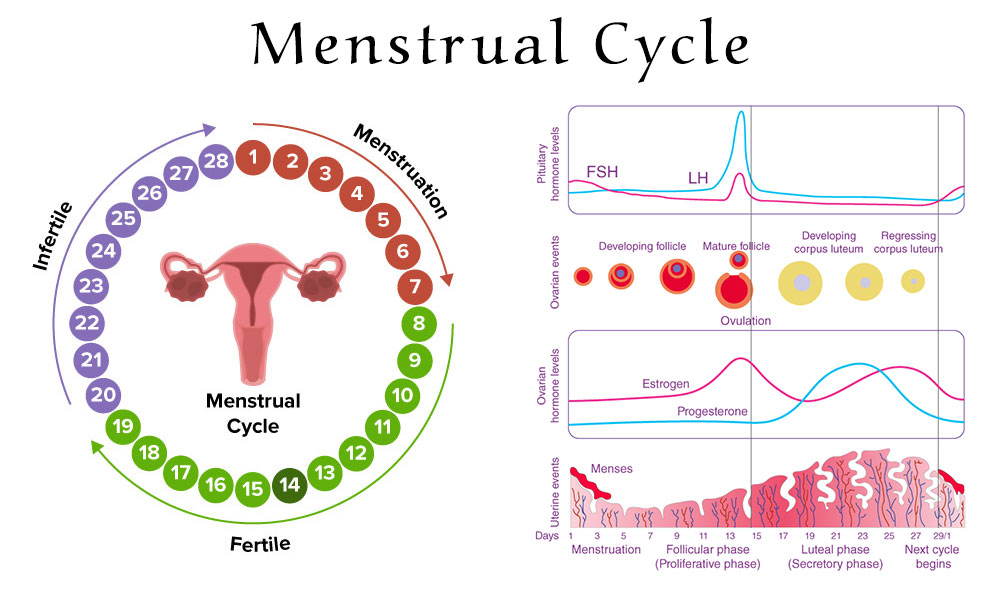
The menstrual cycle has four main phases: menstrual, follicular, ovulation, and luteal.
- Menstrual Phase
- What Happens: This is when you get your period. The lining of the uterus sheds, causing bleeding.
- Duration: About 3 to 7 days.
- Symptoms: Cramps, bloating, tiredness, and mood swings.
- Follicular Phase
- What Happens: The body prepares an egg for release. The lining of the uterus starts to thicken again.
- Duration: Starts on the first day of the menstrual cycle and lasts until ovulation (around 14 days).
- Symptoms: Increased energy, improved mood, clearer skin.
- Ovulation Phase
- What Happens: The ovary releases a mature egg into the fallopian tube.
- Duration: Around day 14 of a 28-day cycle, but can vary.
- Symptoms: A slight fever, clear stretchy vaginal discharge, and mild cramps.
- Luteal Phase
- What Happens: The body prepares for a possible pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus begins to break down.
- Duration: About 14 days.
- Symptoms: Bloating, breast tenderness, mood changes, food cravings.
Hormonal Changes
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle. The key hormones involved are:
- Estrogen
- Role: Helps thicken the uterine lining during the Follicular Phase.
- Symptoms of Imbalance: Weight gain, mood swings, fatigue.
- Progesterone
- Role: Stabilizes the uterine lining during the luteal phase.
- Symptoms of imbalance: irregular periods, headaches, mood changes.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Role: Triggers ovulation (release of the egg).
- Symptoms of Imbalance: Fertility issues, irregular periods.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Role: Stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles (eggs).
- Symptoms of Imbalance: Irregular periods, ovulation problems.
Managing Symptoms
Understanding your cycle can help manage symptoms better. Here are some tips:
- For Cramps: Use a heating pad, take pain relievers, stay active.
- For Bloating: Eat a balanced diet, drink plenty of water, avoid salty foods.
- For mood swings: Relax, sleep enough, and talk to a friend or therapist.
- To combat Fatigue: Focus on rest, eat a balanced diet, engage in routine physical activity.
Understanding the menstrual cycle empowers women to take control of their health. Knowing the phases, symptoms, and hormonal changes can help you. You can better manage your cycle and well-being. If you have concerns about your menstrual cycle, consult a healthcare professional.