Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): Causes, Symptoms, and Risks
What are STDs?
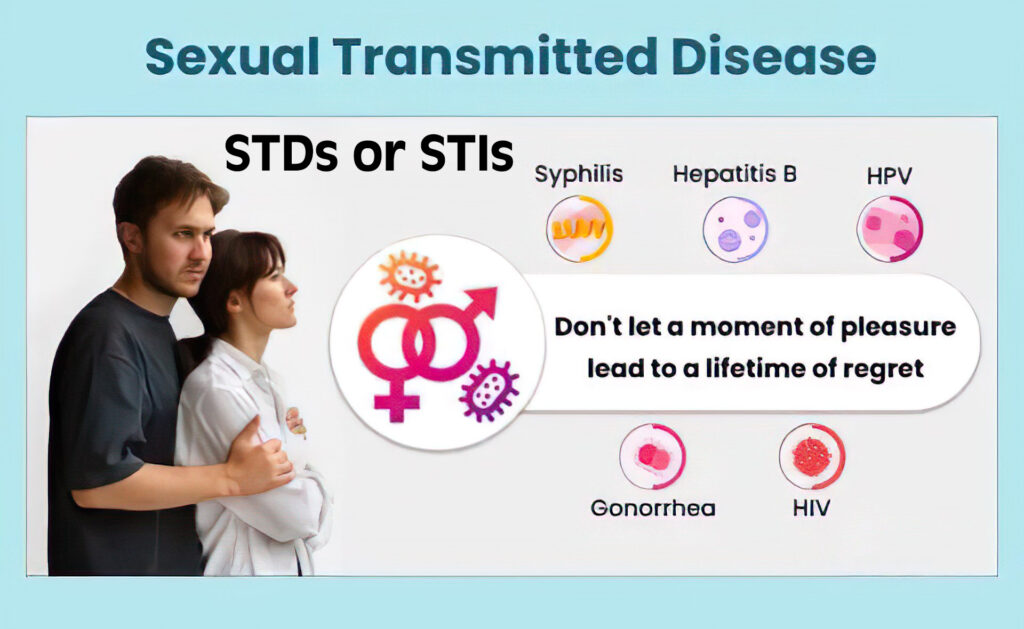
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), also called sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are infections that spread through sexual contact, including anal, vaginal, or oral sex. They can be caused by bacteria, parasites, or viruses. Sometimes, people with STDs don't show any symptoms, so they might not know they are infected.
Common STDs and Their Symptoms:
Bacterial STDs:
- Gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia
- Symptoms: Sores or bumps on the genitals, painful urination, unusual discharge.
Parasitic STD:
- Trichomoniasis
- Symptoms: Itching, burning, discharge.
Viral STDs:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Causes genital warts, can lead to cervical cancer.
- Herpes simplex virus: Causes painful sores.
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): Leads to AIDS.
- Viral STDs might not show symptoms right away and can take years to appear.
Some STDs don't cause immediate symptoms, but they can lead to serious health problems if not treated. Regular testing and safe sex practices are important to prevent and detect STDs early.
Causes of STDs:
- Bacteria: Gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia.
- Parasites: Trichomoniasis.
- Viruses: HPV, herpes simplex virus, HIV.
Risk Factors:
- Unprotected sex: Not using condoms during vaginal or anal sex increases the risk.
- Multiple sexual partners: More partners mean higher exposure.
- Sharing needles: Using needles with others can spread infections.
- Pregnancy or childbirth: Some STDs can be passed from mother to baby.
When to Seek Medical Help:
- If you’re sexually active and think you might have been exposed to an STD.
- If you have any symptoms of an STD.
Early detection and safe practices are key to maintaining sexual health. See a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.